**Mastery Loadouts**
Due to issues related to the release of Mastery Loadouts, the "free swap" period will be extended.
The new end date will be May 1st.
Due to issues related to the release of Mastery Loadouts, the "free swap" period will be extended.
The new end date will be May 1st.
Options
Arena Crystal Comparison
Ever wondered which one is more reliable for units? I compared UC vs regular with a pretty large sample size to see the difference.
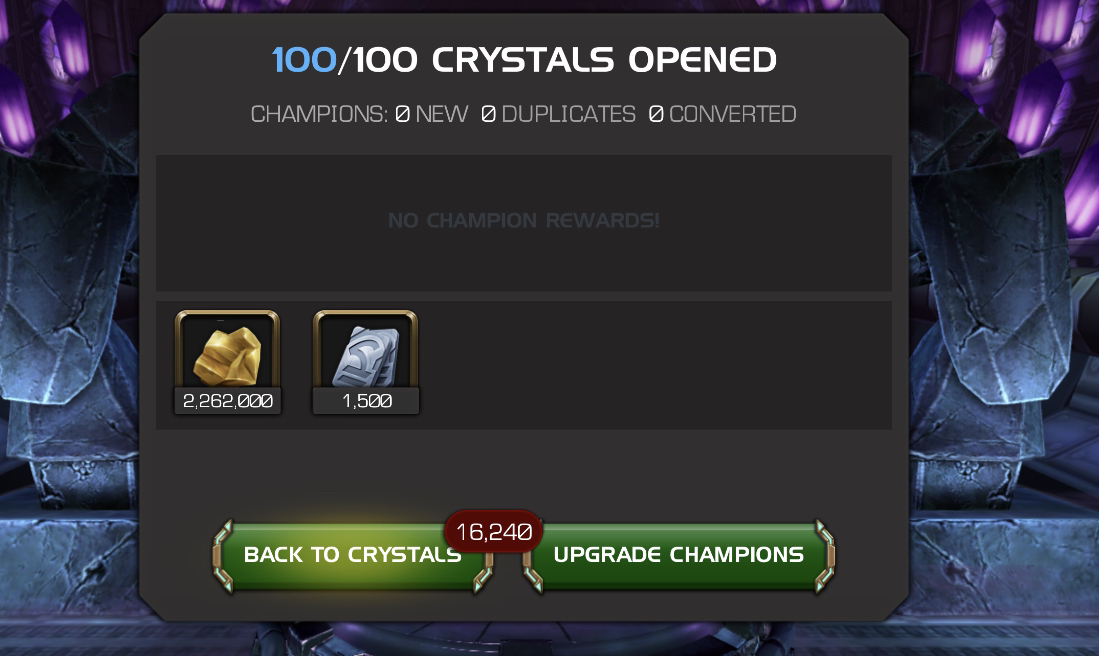

I’ve seen many people make claims that they average out to be the same, but this typically isn’t true, as you can see from the screenshots. Statistically it would be true if you had a really really large sample size, but in most cases that isn’t practical.
You can think of it another way. In Calculus, the Riemann Sum is used to approximate the area under a curve between two points x=a and x=b. As n approaches infinity (the number of partitions), the Riemann sum approaches the definite integral between a and b.


I’ve seen many people make claims that they average out to be the same, but this typically isn’t true, as you can see from the screenshots. Statistically it would be true if you had a really really large sample size, but in most cases that isn’t practical.
You can think of it another way. In Calculus, the Riemann Sum is used to approximate the area under a curve between two points x=a and x=b. As n approaches infinity (the number of partitions), the Riemann sum approaches the definite integral between a and b.
0

